DIPLOMA IN MARITIME STUDIES, INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY
ACADEMIC REGULATIONS
Organization of Academic Programmes
The Diploma in Maritime & ICT shall be a two-year programme. Each academic session is made up of two semesters. At the end of the first year (have referred) to as year I. The students are sent out for the mandatory minimum of two (2) months Industrial Training Programme. It is compulsory that students pass this industrial training after submitting logbook and assessing the report. Year 1 and 2 of this programme have equal weighting of 50% as shown in Table 1
NEWLY APPROVED PROGRAMMES IN THE CENTRE
• Diploma in Maritime Studies, Informaiton and COmmunition Technology
• Diploma in Marine Drilling and Production Technology
• Diploma in Industrial Welding and Fabricaiton Technology
• Diploma Project Management Techonology
• Diploma in Computing and Computer Techonology
Course Adviser
Each student shall be assigned to a Course Adviser appointed by the Director. The course Adviser in conjunction with the Administrative officer shall be responsible for grading the student in the correct courses, fulfilling the regulations and shall also advice the students generally on all related academic matters.
Examinations
All courses are accessed using examinations, continuous assessments and laboratory/practical work at the end of each semester. Projects are based on written reports and/or oral defense.
Other Categories
The following are other categories which a student’s status may be classified at the end of the session; which are not dependent on the total number of credits earned.
- Voluntary Withdrawal: A student who has applied for voluntary withdrawal or failed to register for the session is deemed to have voluntarily withdrawn. Student who has applied for voluntary withdrawal enjoys it only for the approved period unless such application is renewed and approved.
- Disciplinary/Misconduct cases: The results of any student with pending disciplinary or examination misconduct cases are usually withheld until the determination of the cases.
- Medical Cases: Astudent with a genuine medical case may apply to repeat courses for examination missed with proper documentation.
- Special Cases: Any case that does not fall into the above cases is regarded as a special case.
Note:
a. Any medical case must be reported to the Director of Centre in writing at least 24 hours before the examination.
b. A student who registered for a course but fails to take the examination without an approved reason is deemed to have failed the course.
Processing of Academic Transcripts
Applications for transcripts are usually made to the University through the Examinations and Records Office after payment of the prescribed amount. Such applications are then processed through the Centre. The results in the transcripts are authenticated in the Centre and then forwarded to the Director’s Office for final transmission to the Examinations and Records Office. Applicants are not allowed to handle their transcripts during this processing.
Admission Requirements
Candidates seeking admission into this programme should possess any of the following qualifications:
• Credit in Mathematics with a pass in English Language and credit in three other subjects (Physics, Chemistry, Technical Drawing, Biology/Agricultural Science, Economics/Government and Geography.) at GCE/WAEC/SSCE/NABTEB/NECO
• TC II with credit in Mathematics and a pass in English Language and credit in three other subjects as specified above
• City and Guilds (Part 1) in any area of Engineering
• A qualification equivalent to any of the above.
• Mature candidates with a minimum of pass in mathematics and credit in three other subjects as specified above at GCE/WAEC/SSCE/NABTEB/NECO with not less than five years of cognate experience in industry.
Programme Duration
A student must have met the minimum of two (2) years and a maximum of four (4) years required for graduation.
Internal Examinations - A candidate must earn a minimum of 20 credits at the end of the session to move to the next year.
- Any candidate who earns between 10 and 19 credits at the end of any session must register to repeat all the courses (including those passed for the session) during the next session (i.e. the student will have to probate)
- A candidate who earns less than 10 credits in a session is deemed to have failed and is required to withdraw from the programme.
- A candidate who has exhausted the maximum four (4) years for the programme is also required to withdraw from the programme.
Entrance Examination
No entrance examination, Admission is base on ‘O’ level reqirement, candidate must have a credit pass in Physics, Mathematics, Chemistry, with a pass in English Language.
Lecture Periods
Lectures shall take place from Monday to Friday between the hours of 2.00 and 6.00pm. Practicals (laboratories and workshop practices) will however be scheduled between the hours of 9.00am to 12.00 noon Monday to Friday or/and Saturdays as may be appropriate.Industrial Training
The students must undertake and pass a three-month industrial training period between the first and second years of the programme. Meaning students are expected to submit report for grading.
Grading
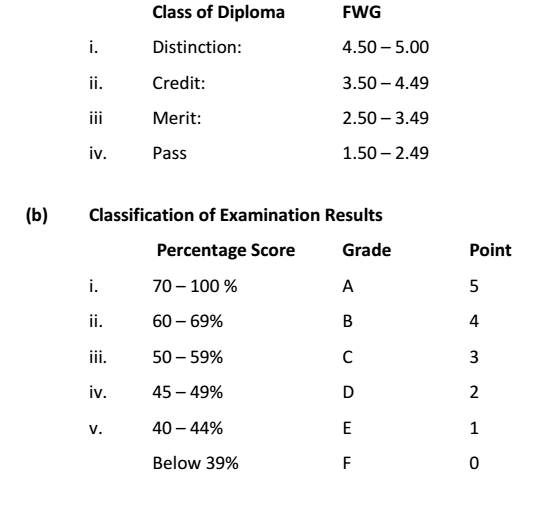
The Diploma Classification is to follow the standard diploma classification using the University of Benin final weighted grade as follows:
(a) Classification of Diploma Result from 2008 to date
Guidelines on the Registration of Courses
- Students are required to register manually for now with the Centre for the full session at the beginning of each session
- The maximum credits allowed is 30 credits for a semester and 50 credits for a session.
- Students must register the failed/trailed courses first
- students can only be registered for a course after taking the prerequisites (if any) for that course
- All courses are mandatory for the students to graduate and so the issue of change of course is not in place.
Graduation Requirement
A student must have passed all the required courses and undergo industrial training, pass all computer pratical courses (ELA)
Final Weighted Grade
Each of the levels of the normal two-year diploma programme is weighted separately for the purpose of calculating the class of diploma at graduation. The weightings depend on the level of year of entry as shown in Table 1
Table 1: Weighting of Levels
| Year | Rating | 2 Year Diploma |
| 100 | R1 | 0.50 |
| 200 | R2 | 0.50 |
The final GPA for a graduating student is known as the Final Weighted grade (FWG). This calculation depends also on the year or level of entry into the programme as shown in Table 2
Table 2: Grade Point Average
| Number of Years | Final Weighted Grade (FWG) |
| 2 Year Diploma Programme | R1 GPA1 + R2 GPA2 |
Where R1, R2 are as in Table 1 while GPA1, GPA2 are the GPAs for Years 1 to 2 respectively.
STAFF PROFILE
| S/N | NAME | QUALIFICATION | DESIGNATION |
| 1 | Dr. D. O. Onaiwu | Ph.D Petroleum Eng. (UNIPORT, 2017) M. Eng. Petroleum Eng. (UNIBEN, 2012), B.Eng. Petroleum Eng. (2006) Dip. Computer Eng. (2002) | Director of Centre |
| 2 | Dr. R.S. Ebhojiaye | Ph.D . Manufacturing Eng. (UNIBEN, 2017), M. Eng. Manufacturing Eng., (UNIBEN, 2013, B.Eng. Production Eng. (UNIBEN, 2007). | Assistant Director of Centre |
| 3 | Mrs. S. Jerry-Orhue | M.P.A. (UNIBEN, 2016) B.A. Philosophy (UNIBEN, 2000). | Administration of Centre |
| 4 | Mrs. A. Best-Idahosa | B.Sc Public Administration (UNIBEN, 2016). | Senior Machine Room Supervisor II |
| 5 | Okhueleigbe Timothy Abhulimhen | Higher Diploma, Secretarial Studies (2015) Diploma, Secretarial Studies (2014). | Confidential Secretary |
| 6 | Mr. Egbon Christopher Osas | B.Sc Agric Econs and Extension (UNIBEN, 2016)Diploma Agric Econs and Extension (UNIBEN, 2007). | Public Relations Officer of the Centre. |
| 7 | Mrs. Omonigho Asibor | B.Sc Local Government Administration (UNIBEN, 2014). Diploma Public Administration (2003). | Industrial Training Liaison Officer |
| 8 | Mr. Omonomose Patrick Iyobosa | B.A. Philosophy (UNIBEN, 2008). Diploma in Comp. Eng, (2009). | System Analyst/Technician |
| 9. | Okeke Chika Kennedy | B.Sc (Ed) (UNIBEN, 2015). Diploma in Comp. Science (2011). | Business Developer |
| 10. | Mr. Ibenyenwa Ifechukwu Timothy | Telecommunicaiton Power (Huawei University, China, 2017) Higher National Diploma, Mechanical Eng. (2015). National Diploma, Mechanical Eng. (2012) | System Analyst |
| 11. | Ogbemudia Godwin Moses | Diploma in Accounting (Jos, 2008) | Accounting Officer/Tally Clerk |
| 12. | Omorodion Osayomore Catherine | NCE Computer Science/Economics (2014) | Executive Officer |
| 13. | Obaseki Frankyn Nosakhare | Certificate in Health Information Management (HIM) (2014), Certificate in Graphic Designs, Desktop Publishing and ICT (2019) | Assistant Systems Analyst |
| 14. | Mrs. Rachael Eriamen | S.S.C.E. (NECO) (2008) | Computer Lab Assistant |
| 15. | Mrs. Vero Igiebor | Primary School Leaving Certificate | Officer Assistant |
COURSE STRUCTURE
Year One
| Semester | Course Code | Course Title | Hours per Week | Course Credit |
| 1ST | EMA 011 | Algebra and Statistics | 3 | 3 |
| ECH 011 | General Chemistry | 3 | 3 | |
| EPH 011 | Mechanics of Materials | 3 | 3 | |
| END 011 | Engineering Drawing I | 2 | 2 | |
| ELA 011 | Workshop Technology and Practice I | 1 | 2 | |
| DMT 011 | Introduction to Port Operations | 3 | 3 | |
| DMT021 | Introduction to Maritime Trade and Shipping Documentation | 3 | 3 | |
| Total Credits | 18 | 19 | ||
| 2ND | EMA 012 | Geometry and Trigonometry | 3 | 3 |
| ECH 012 | Physical Chemistry | 3 | 3 | |
| EPH 012 | Heat, Optics, Waves and Sound | 3 | 3 | |
| END 012 | Engineering Drawing II | 1 | 2 | |
| ELA 012 | Workshop Technology and Practice II | 1 | 2 | |
| DMT 012 | Computer Software I | 1 | 2 | |
| DMT 022 | Computer Hardware I | 3 | 3 | |
| DMT 032 | International Trade | 2 | 2 | |
| Total Credits | 17 | 20 | ||
| INDUSTRIAL TRAINING (BETWEEN YEAR I AND YEAR II) |
L: Lecture hour; T: Tutorial hour; P: Practical hour
Year Two
| Semester | Course Code | Course Title | Hours per Week | Course Credit |
| 1ST | EMA 021 | Calculus and Differential Equations | 2 | 3 |
| ECH 021 | Organic Chemistry | 2 | 3 | |
| EPH 021 | Electromagnetism and Modern Physics | 2 | 3 | |
| ELA 021 | Workshop Technology and Practice III | 1 | 2 | |
| DMT 031 | Oil Tankers | 2 | 3 | |
| DMT 041 | Shipping Routes and Law of the Sea | 2 | 3 | |
| DMT 051 | Ships and Cargoes | 2 | 3 | |
| Total Credits | 13 | 20 | ||
| 2ND | DMT 042 | Computer Software II | 3 | 3 |
| DMT 052 | Computer Hardware II | 2 | 3 | |
| DMT 062 | Oil Spillage, Prevention and Control | 3 | 3 | |
| DMT 072 | Carbot age Law | 2 | 2 | |
| DMT 082 | Improving Port Performance | 2 | 2 | |
| DMT 092 | Networking and Instrumentation | 3 | 3 | |
| DMT 099 | Project | 3 | 3 | |
| Total Credits | 18 | 19 |
L: Lecture hour; T: Tutorial hour; P: Practical hour
COURSE CONTENT
Year One
EMA011: ALGEBRA AND STATISTICS (3 CREDITS)
Real number system: Rational and irrational numbers. Mathematical induction. Real sequences and series: elementary notions of convergence of geometric, arithmetic and other simpler series. Theory of quadratic equations. Simple inequalities: absolute value and time triangle inequality. Identities. Partial fractions. Sets and subsets: union, intersection and compliments. Properties of some binary operations of sets: addition and factor
formulae. Distributive, closure, associative and cumulative laws. Relations in a set: equivalence relation. Properties of set functions and inverse set functions. Permutations and combinations. Diagrammatic representation of descriptive data: measures of location and dispersion of group data. Problems of grouping. Associated graphs. Introduction to probability. Binomial distribution. Linear correlation: scatter diagram, product – moment and rank correlation. Linear regression.
ECH011: GENERAL CHEMISTRY (3 CREDITS)
Introduction to General Chemistry
Atoms, molecules, isotopes, Avogadro’s number, mole concept, Dalton’s theory, modern concepts of atomic theory, laws of Chemical combination, relative atomic masses.
The states of matter: gases (gas laws, general gas equation), liquids and solids (lattice structure, isomorphism, giant molecules).
Introduction to Organic Chemistry
(i) Definitions, classification of organic compounds; homologous series, functional groups.
(ii) General procedure of isolation and purification of organic compounds.
(iii) Determination of structure of organic compounds. Elemental analysis, percentage composition, empirical and molecular formula, structural formula.
(iv) Isomerism. Structural isomerism and stereoisomerism.
(v) Electronic theory in organic chemistry. Atomic models, quantum number; atomic orbital. Hybridization leading to formation of carbon, carbon single, double and triple bonds. Hydrogen bonding, electro-negativity, dipole moment. Polarisation, bond energy. Inductive and resonance effects. Hyper conjugation. Bond length. Carbonium ions and carbanions
(vi) Nomenclature – common (trivial) names. IUPAC names of classes of compounds.
EPH011:MECHANICS AND MATERIAL SCIENCE (3 CREDITS)
Scalar and Vectors: Addition and resolution of vectors, rectilinear motion and Newton’s law of motion, depleting forces and circular motion, gravitational mass, free fall: projectile motion, Newton’s law of gravitational potential, potential well.
Momentum and the conservation of momentum, work, power and energy. Potential energy for a gravitational field, and elastic bodies, kinetic energy.
Mechanical isolation of bodies, free body diagram conditions for equilibrium of co-planar and three-dimensional force systems.
Concept of unaxial stress and strain, typical stress-strain curves in tensile testing. Hook’s laws; modulus of elasticity, point, ultimate strength etc, liquids, solids and gases
END011: ENGINEERING DRAWING 1 (2 CREDITS)
Introduction: Types of Engineering Drawings, Draughting materials and Equipment.Types of lines and lettering, geometrical construction, principle of tangency, loci, orthographic projection.
DMT011: INTRODUCTION TO PORT OPERATIONS (2 CREDITS)
Definition, classification, various types and alternatives to the formal port. Tides and ship draft. Number of berths required. Congestion. Berth layout and a comparison between different types. Specialised terminals. Types of ownership. Port charges. Port labour and ship canals.
DMT021: INTRODUCTION TO MARITIME TRADE AND SHIPPING DOUCMENTATION (3 CREDITS)
Growth of shipping and national fleets. International shipping constraints. Flags of convenience. Shipping contribution to balance of payment. Flags of discrimination. Subsidies, liner conferences, tonnage stabilisation schemes. Liner freight rate. Bill of lading, letter of credit. Types of delivery (FOB, CIF, C&F)
EMA012: GEOMETRY AND TRIGONOMETRY (3 CREDITS)
Two-dimensional co- ordinate geometry, straight lines, angle between two lines, distance between points. Equations of circle, tangent and normal or a circle. Properties of parabola, ellipse, hyperbola. Straight lines and planes in space, direction cosines; angle between lines and between lines and planes, distance of a point from a plane, distance between two skew lines. Circular measure trigonometric functions of angles of any magnitude.
ECH012: PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY (3 CREDITS)
Hydrogen and hydrides, peroxides, chemistry of groups 0,I, II elements. Acids, bases and salts. Acid – base properties of oxides, quantitative and qualitative analysis. Volumetric analysis, mole molarity. Behaviour of electrolytes. Water, colligative properties. Oswald’s dilution law. Arrhenius, Bronsted – Lowry,
Lewis concept and application. Buffers. Introduction to reaction rates. Equilibria and equilibrium constants. Common ion effects. Precipitation reactions. Nuclear binding energy, fission and fusion. Introduction of nuclear chemistry.
EPH012: HEAT, OPTICS, WAVES AND SOUND (3 CREDITS)
Temperature, heat work: heat capacities, second law, Carnot cycle, Thermal conductivity, Stefan’s law. Wave and light, mirrors, lenses, formation of images, thin lenses in contact. Types of waves. Reflection and refraction of waves, stationary waves, diffraction, fiber optics, dispersion, interference, coherence and polarization. Propagation of sound in solid, Liquids and gases. Poppler effect.
END012: ENGINEERING DRAWING II (2 CREDITS)
Dimensioning, sectional views, conventions, true lengths, technical sketching, civil, mechanical and electrical engineering drawing practice.
ELA012: WORKSHOP TECHNOLOGY AND PRACTICE II (2 CREDITS)
The Engineer in practice. Basic production Processes. Types of engineering workshops, including jobbing, batch and mass production. Engineering materials. Safety in engineering practice. Marking out and measurement in the workshop, machine shop technology and practice.
DMT012: COMPUTER SOFTWARE (2 CREDITS)
Definition. Operating systems. Application software. High level languages. Identify input and output units. Storage units. CPU. (Central Processing Unit). Different types of software. System software. Application software. Low and high-level languages. Their impact on the office environment.
DMT022: COMPUTER HARDWARE I (3 CREDITS)
Identifying all different parts of the computer. Full description of all parts and their interaction within the system. Trouble shooting.
Main board types and identifications. Functions & components. System casing. Installing and Upgrading. Testing. Electronics basics. Static electricity. Power supply functions/connectors. Form factors. PC Ratings. Soft switches. G/Power signals. G/Power supply testing and trouble shooting. Blackouts. Power surges. Line noise. Spikes. System Bus types/ features. Questions and answers
DMT032: INTERNATIONAL TRADE (2 CREDITS)
Definition. Trading between countries. Balance of trade and Balance of payment. Protectionism.
Year Two
EMA021: CALCULUS AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS (3 CREDITS)
Simple functions of a single real variable and their graphs, continuity, limit. Graphs of simple functions: polynomials, rational, trigonometric, etc. Rate of change, tangent and normal to a curve. Differentiation of functions. Rules of function differentiation. Stationary values of simple functions: integration
by substitution and by parts – definite integrals, volume of revolution, and area of surface of revolution. Differential equations: formation of differential equation of first degree and first order of type: variables, separable, exact, homogenous and linear.
ECH021: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (3 CREDITS)
on-polar functional group chemistry: alkanes, alkynes; structure, physical properties, reactions and mechanisms, stereoisomerism. Benzene: structure and aromaticity. Introduction to electrophilic substitution reactions.
Polar functional group chemistry: hydroxyl group: alcohols and phenols; carbonyl group aldehydes and ketones; carbocyclic group – monocarboxylic acids derivatives, i.e. anhydrides. Acid halides,
esters and amides; amino group – amines. Structures: physical properties, important methods of preparation and important methods of preparation and important reactions including mechanisms. Tests and importance. Fats and oils, amino acids, proteins, carbohydrates. Definitions, importance. Nomenclature and classifications, structure and reactions. Natural products, steroids, terpernoids alkaloids. Prostaglandis: definitions, importance and examples.
ELA021: WORKSHOP TECHNOLOGY AND PRACTICE (2 CREDITS)
Presentation of Experimental Data and Analysis. Technical Writing and Report presentation.
EPH021: ELECTROMAGNETISM AND MODERN PHYSICS (3 CREDITS)
Properties of ferrous metals and semi-conductors (silicon and Germanium). Quantum electrodynamics (Einstein’s theory and discovery). Electric field. Magnetic field. Young’s equations steady direct current, Kirchoff Laws. Capacitors, Alternating
current and circuit. Electromagnetic induction, electricity and matter structure of atoms. Atomic theory, X-rays, Planck – Einstein quantum theory. Rutherford atom model, Bohr’s atom model. Hosenberg uncertainty principle, Isotopes, particle emission, gamma radiation, lasers, superconductivity.
DMT031: OIL TANKERS (3 CREDITS)
Introduction and Definition. Crude Oil Products Shuttle Tankers. Petroleum Tankers. Chemical Parcel Tankers
DMT041: SHIPPING ROUTES AND LAW OF THE SEA (2 CREDITS)
The master’s choice of routes. The shortest way and the simplest way. This should be on the discretion of the master of the ship. (The great circle routes as appears on the Mercator chart, the basic navigational chart as a curved line). Use of Modern navigation hardware, such as GPS. (Global positioning system). Origins of Maritime Law. The English court system. Precedent. Arbitration. General characteristic of maritime law. Admiralty Jurisdiction. Other Special Jurisdiction. Law of contract. Hague visible rules following an international maritime convention. Contract of indemnity. Double insurance contribution. Voyage policy on goods. Utmost good faith. Insurable interest. General average. Act of God. Seaworthiness.
DMT051: SHIPS AND CARGOES (INCLUDING HAZARDOUS CARGOES) (3 CREDITS)
Oil Tankers. Chemical Tankers. Dry cargo ships. Double Hull Tankers. Refrigerated cargoes. Bulk cargoes. Dangerous cargoes and deck cargoes.
DMT042: COMPUTER SOFTWARE II (2 CREDITS)
Advanced word-processing. Advanced spreadsheet using Excel. Presentation using PowerPoint. Relational database using Access. Desktop publishing using Corel Draw. Web-design using HTML. Computerized accounting using Sage.
DMT052: COMPUTER HARDWARE II (3 CREDITS)
Candidate should be able to complete the following: Maintain ICT equipment and Systems. Customer support provision. Install and configure equipment and operating systems. Install, configure and maintain software. Carry out Systems testing. System monitoring and operation. Repair centre procedure. Networking
DMT062: OIL SPILLAGE, PREVENTION AND CONTROL (3 CREDITS)
Types of oil spillage and causes. The effect on: – The environment. Marine life and the population or the inhabitants. Preventative measures, combative techniques and clean-ups.
DMT072: INTRODUCTION TO NIGERIAN MARITIME CABOTAGE POLICY AND LAW (2 CREDITS)
- Definition: various forms and comparative national application of cabotage and benefits.
- Coastal and Inland shipping (cabotage) Act, 2003. Coastwise shipping Laws (the JONES ACT, 1920).
- Nigerian Coastline and Inland waterways. Ports and locations. Domestic shipping policy. National flags.
- Types of Vessels, Types of Cargo, Cargo support and Cargo availability.
- Seaman’s Rights.
DMT082: IMPROVING PORT PERFORMANCE (2 CREDITS)
For a port to be efficient it requires a well-trained labour force and adequate equipment.- Adequate labour force
- Modern lifting gears and regular maintenance of all equipment.
- Regular training of senior and junior staff
- Regular inspection of all equipment by health and safety executives.
- well maintained berths and ware-housing
- Adequate lighting and good stacking of goods for easy access
DMT092: NETWORKING & INSTRUMENTATION (3 CREDITS)
tarting Up Router Startup. Router Modes. Help & Editing. Terminal History Enhanced Editing. Router Status. Configuring Banners. MOTD Banner. EXEC Banner. Login Banner. Line Configuration. Console Configuration. Auxiliary, configuration. Virtual Terminal Configuration. Passwords and Identification. Setting Hostname. Managing Passwords. Configuring Interfaces. Configuring Serial Interface.
Managing Domain & more. Domain Configuration. Host Name
Mapping. Name Server & Http Server. Routing Protocols. RIP Routing. IGRP Routing. Managing IP Routing. Enabling/Disabling CDP. Test Connectivity. Managing ACL. Defining ACL. Applying ACL Process Control. Power, Energy & Environment. Instrumentation. Technical Articles.
IEC61131-3PLC Programming standard
PLC Programming Articles
Documenting Industrial Control Systems
DMT099: PROJECT (3 CREDITS)
Students are to write a Project of not less than three thousand (3,000) words on oil spillage and control. Students may choose any related topic of their choice in Maritime Studies or Information and Communication Technology.- Students Assessment
- Address, websites, email
- Add: Every effort has been made to ensure the correctness of the information contained in this handbook. The Centre will however, not take responsibilities for any errors or inaccuracies. Some of the information contained in this handbook are subject to change by the Centre or the university at any time without prior notice.
NEWLY APPROVED COURSES INCENTRE FOR MARITIME STUDIES, INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY - Marine Drilling and Production Technology
- Industrial Welding and Fabrication Technology
- Project Management Technology
- Computing and Computer Technology
All proposed programmes are to be resident in the above-mentioned center and all other information regarding admission requirements and grading procedures are the same as it is in the Center for Maritime Studies, Information and Communication Technology.
Year One Diploma in Marine Drilling and Production Technology
| SEMESTER | COURSE CODE | COURSE TITLE | L | T | P | CREDIT LOAD |
| 1ST | EMA 011 | Algebra and Statistics | 2 | 1 | – | 3 |
| ECH 011 | General Chemistry | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| EPH 011 | Mechanics of Materials | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| END 011 | Engineering Drawing I | 1 | 1 | – | 2 | |
| ELA 011 | Introduction Technology & Practice I | 1 | – | 3 | 2 | |
| DPT 011 | Introduction to Petroleum Engineering | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| DPT 013 | Introduction to Petroleum Geology | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| DPT 015 | Principle of Well Construction | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| TOTAL CREDIT | 22 | |||||
| 2ND | EMA 012 | Geometry and Trigonometry | 2 | 1 | – | 3 |
| ECH 012 | Physical Chemistry | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| EPH 012 | Heat Optics, Wave and Sound | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| END 012 | Engineering Drawing II | 1 | 1 | – | 2 | |
| ELA 012 | Workshop Technology & Practice II | 1 | – | 3 | 2 | |
| DPT 012 | Production Economics | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| DPT 014 | Drilling and Well Completion | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| DPT 016 | Offshore / Deepwater Drilling | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| DPT 018 | Casing Design | 1 | 1 | – | 2 | |
| TOTAL CREDIT | 24 |
Year Two Diploma in Marine Drilling and Production Technology
| SEMESTER | COURSE CODE | COURSE TITLE | L | T | P | CREDIT LOAD |
| 1ST | EMA 021 | Calculus and Differential Equation | 2 | 1 | – | 3 |
| ECH 021 | Organic Chemistry | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| EPH 021 | Electromagnetism and Modern Physics | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| ELA 021 | Workshop Technology & Practice III | 1 | – | 1 | 2 | |
| DPT 021 | Well Completion and Workovers | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| DPT 023 | Regulatory Issues for Oil & Gas Industry | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| DPT 025 | Production and Recovery | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| DPT 027 | Computers Applications for the Oil and Gas Industry | 2 | 1 | – | 2 | |
| TOTAL CREDIT | 23 | |||||
| 2ND | DPT 022 | Production Technology | 2 | 1 | – | 3 |
| DPT 024 | Introduction to Reservoir Geophysics | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| DPT 026 | Rock Geomechanics | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| DPT 028 | Drilling Fluid / Mud Engineering | 2 | 1 | – | 2 | |
| DPT 030 | Surface Production & Equipment | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| DPT 032 | Petroleum Geology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | |
| DPT 034 | Laboratory Practice | 2 | – | – | 3 | |
| DPT 036 | Offshore Drilling and Production Equipment | 2 | 1 | – | 2 | |
| DPT 300 | Project | 6 | ||||
| TOTAL CREDIT | 28 |
Year One Diploma in Industrial Welding and Fabrication Technology
| SEMESTER | COURSECODE | COURSE TITLE | L | T | P | COURSE CREDIT |
| 1ST | EMA 011 ECH 011 EPH 011 END 011 ELA 011 DWF 011 DWF 013 | Algebra and Statistics General Chemistry Mechanics of Materials Engineering Drawing 1 Workshop Technology &Practice 1 Introduction to Design Fabrication Techniques | 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 | 1 1 1 1 – – – | – – – 2 3 6 6 | 3 3 3 2 2 3 3 |
| TOTAL CREDIT | 19 | |||||
| 2ND | EMA 012 ECH 012 EPH 012 END 012 ELA 012 DWF 012 DWF 014 DWF016 DWF018 | Geometry and Trigonometry Physical Chemistry Heat, Optic, Wave and Sound Engineering Drawing 11 Workshop Technology &Practice 11 Introduction to Shop Practice Graphical Communication Computer Software Computer Hardware | 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 2 | 1 1 1 1 – – – – 1 | – – – 3 3 6 6 3 – | 3 3 3 2 2 3 3 2 2 |
| TOTAL CREDIT | 23 |
Year Two Diploma in Industrial Welding andFabrication Technology
| SEMESTER | COURSECODE | COURSE TITLE | L | T | P | COURSE CREDIT |
| 1ST | EMA 021 ECH 021 EPH 021 ELA 021 DWF 041 DWF 051 DWF 061 DWF 071 | Calculus and Differential Equation Organic Chemistry Electromagnetism &Modern Physics Workshop Technology &Practice Introduction to CAD/CAM The Design Project Computer Appreciationin Welding Safety in Welding Engineering | 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 2 | 1 1 1 1 1 1 | – – – 3 | 3 3 3 2 3 3 2 3 |
| Total Credit | 22 | |||||
| 2ND | DWF 042 DWF 052 DWF 062 DWF 072 DWF 082 DWF 092 DWF094 DWF 099 | Computer Application in Welding Brazing and Soldering Welding and Joining Metallurgy Welding Processes and Control Stress Corrosion and Cracking of Materials Welding Design and Equipment Fundamentals of Pipeline Design and Construction Project | 1 2 1 2 1 1 1 – | – – – 1 – – – – | 3 1 6 – 6 – 6 9 | 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 |
| Total Credit | 23 |
Year One Diploma in Project Management Technology
| SEMESTER | COURSE CODE | COURSE TITLE | L | T | P | CREDIT LOAD |
| 1ST | EMA011 ECH011 EPH011 END011 ELA011 PMT011 PMT013 PMT015 NAM045 | Algebra and Statistics General Chemistry Mechanics of Material Engineering Drawing I Workshop Technology & Practice I Introduction to Engineering Material Principles of Management Introduction to Project Management Technology Basic Accounting | 2 2 2 1 1 2 1 2 1 | 1 1 1 1 – 1 1 1 1 | – – – – 3 – – – – | 3 3 3 2 2 3 2 3 2 |
| TOTAL CREDIT | 23 | |||||
| 2ND | EMA012 ECH012 EPH012 END012 ELA012 PMT012 PMT014 NAM044 NAM046 | Geometry and Trigonometry Physical Chemistry Heat, Optics, Wave and Sound Engineering Drawing II Workshop Technology & Principle II Quality Management and Control Computer Software Computer Hardware Introduction to Electrical Technology | 2 2 2 1 1 2 1 1 2 | 1 1 1 1 – 1 1 – 1 | – – – – 3 – – – 3 | 3 3 3 2 2 3 2 3 2 |
| TOTAL CREDIT | 23 |
Year Two Diploma in Project Management Technology
| SEMESTER | COURSE CODE | COURSE TITLE | L | T | P | CREDIT LOAD |
| 1ST | EMA021 ECH021 EPH021 ELA021 PMT021 PMT023 PMT025 PMT015 PMT029 | Calculus and Differential Equation Organic Chemistry Electromagnetism and Modern Physics Workshop Technology & Practice I Material Management Financial Accounting Industrial Location Construction Materials Principles of Engineering Survey | 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 2 2 | 1 1 1 1 – 1 1 1 1 | – – – – 3 – – – – | 3 3 3 2 2 2 2 3 3 |
| TOTAL CREDIT | 23 | |||||
| 2ND | PMT022 PMT024 PMT026 PMT026 PMT030 PMT032 PMT034 PMT036 PMT038 PMT200 | Taxation Marketing Management Operation Research Project Planning and Control Transport Infrastructural Planning Strategic Management Project Design &EIS Maintenance Management Management of Information System Project | 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 – | 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 – | – – – – – – – – 9 | 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 3 2 3 |
| TOTAL CREDIT | 24 |
Year One Diploma in Computing & Computer Technology
| SEMESTER | COURSE CODE | COURSE TITLE | L | T | P | CREDIT LOAD | |
| 1ST | EMA 011 | Algebra and Statistics | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| ECH 011 | General Chemistry | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | ||
| EPH 011 | Mechanics of Materials | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | ||
| END 011 | Engineering Drawing I | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | ||
| ELA 011 | Workshop Technology & Practice II | 1 | – | 3 | 2 | ||
| CCT 011 | Computer Fundamentals | 1 | – | 6 | 3 | ||
| CCT 013 | Computer Programming in Computer | 1 | – | 6 | 3 | ||
| CCT 015 | Electrical Engineering | 2 | 1 | – | 2 | ||
| 2ND | TOTAL CREDIT | 21 | |||||
| EMA 012 | Geometry and Trigonometry | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | ||
| ECH 012 | Physical Chemistry | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | ||
| EPH 012 | Heat Optics, Wave and Sound | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | ||
| END 012 | Engineering Drawing II | 1 | 1 | – | 2 | ||
| ELA 012 | Workshop Technology & Practice II | 1 | – | 3 | 2 | ||
| CCT 012 | Logic Circuits | 2 | 1 | – | 2 | ||
| DPT 014 | Object Oriented Programming in C++ | 1 | – | 6 | 3 | ||
| DPT 016 | Wed Technology & Programming I | 1 | – | 6 | 2 | ||
| DPT 018 | Data Mining and Data Warehousing | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | ||
| TOTAL CREDIT | 23 | ||||||
Year Two Diploma in Computing & Computer Technology
| SEMESTER | COURSE CODE | COURSE TITLE | L | T | P | CREDIT LOAD |
| 1ST | EMA 021 | Calculus and Differential Equation | 2 | 1 | – | 3 |
| ECH 021 | Organic Chemistry | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| EPH 021 | Electromagnetism and Modern Physics | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| ELA 021 | Workshop Technology &Practice III | 1 | – | 3 | 2 | |
| CCT 021 | Web Technology and Modern Physics | 1 | _ | 6 | 2 | |
| CCT 023 | Computer Architecture | 2 | 1 | _ | 3 | |
| CCT 025 | Computer Repairs and Maintenance I | 1 | _ | 6 | 2 | |
| CCT 027 | Micro Processors | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| CCT 029 | Electronic Devices and Circuits | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| TOTAL CREDITS | 24 | |||||
| 2ND | CCT 030 | Computer Repairs and Maintenance II | 1 | _ | 6 | 2 |
| CCT 032 | Computer Networks | 1 | _ | 6 | 3 | |
| CCT 034 | Data Structure and Algorithm | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| CCT 036 | Database Management System (DBMS) | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| CCT 038 | Computer Graphic | 1 | _ | 6 | 3 | |
| CCT 040 | Artificial Intelligence | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| CCT 042 | E-Commerce | 2 | 1 | – | 3 | |
| CCT 200 | Project | _ | _ | 9 | 3 | |
| TOTAL CREDITS | 23 |
DIPLOMA IN MARITIME STUDIES, INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY GENERAL COURSES
Year One
EMA011:ALGEBRA AND STATISTICS (3 CREDITS)
Real number system: Rational and irrational numbers. Mathematical induction. Real sequences and series: elementary notions of convergence of geometric, arithmetic and other simpler series. Theory of quadratic equations. Simple inequalities: absolute value and time triangle inequality. Identities. Partial fractions. Sets and subsets: union, intersection and compliments. Properties of some binary operations of sets: addition and factor formulae. Distributive, closure, associative and cumulative laws. Relations in a set: equivalence relation. Properties of set functions and inverse set functions. Permutation and combination. Diagrammatic representation of descriptive data: measures of location and dispersion of group data. Problems of grouping. Associated graphs. Introduction to probability. Binomial distribution. Linear correlation: scatter diagram, product – moment and rank correlation. Linear regression.
ECH011:GENERAL CHEMISTRY (3 CREDITS)
Introduction to General Chemistry
Atoms, molecules, isotopes, Avogadro’s number, mole concept, Dalton’s theory, modern concepts of atomic theory, laws of Chemical combination, relative atomic masses.
The states of matter: gases (gas laws, general gas equation), liquids and solids (lattice structure, isomorphism, giant molecules).
Introduction to Organic Chemistry
(i) Definitions, classification of organic compounds; homologous series, functional groups.
(ii) General procedure of isolation and purification of organic compounds.
(iii) Determination of structure of organic compounds. Elemental analysis, percentage composition, empirical and molecular formula, structural formula.
(iv) Isomerism. Structural isomerism and stereoisomerism.
(v) Electronic theory in organic chemistry. Atomic models, quantum number; atomic orbital. Hybridization leading to formation of carbon, carbon single, double and triple bonds. Hydrogen bonding, electro-negativity, dipole moment. Polarisation, bond energy. Inductive and resonance effects. Hyper conjugation. Bond length. Carbonium ions and carbanions
(vi) Nomenclature – common (trivial) names. IUPAC names of classes of compounds.
EPH011: MECHANICS AND MATERIAL SCIENCE (3 CREDITS)
Scalar and Vectors: Addition and resolution of vectors, rectilinear motion and Newton’s law of motion, depleting forces and circular motion, gravitational mass, free fall: projectile motion, Newton’s law of gravitational potential, potential well.
Momentum and the conservation of momentum, work, power and energy. Potential energy for a gravitational field, and elastic bodies, kinetic energy.
Mechanical isolation of bodies, free body diagram conditions for equilibrium of co-planar and three-dimensional force systems.
Concept of uniaxial stress and strain, typical stress-strain curves in tensile testing. Hook’s laws; modulus of elasticity, point, ultimate strength etc., liquids, solids and gases
END011: ENGINEERING DRAWING 1 (2 CREDITS)
Introduction: Types of Engineering Drawings, Draughting materials and Equipment. Types of lines and lettering, geometrical construction, principle of tangency, loci, orthographic projection.
EMA012: GEOMETRY AND TRIGONOMETRY (3 CREDITS)
Two-dimensional co- ordinate geometry, straight lines, angle between two lines, distance between points. Equations of circle, tangent and normal or a circle. Properties of parabola, ellipse, hyperbola. Straight lines and planes in space, direction cosines; angle between lines and between lines and planes, distance of a point from a plane, distance between two skew lines. Circular measure trigonometric functions of angles of any magnitude.
ECH 012: PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY (3 CREDITS)
Hydrogen and hydrides, peroxides, chemistry of groups 0,I, II elements. Acids, bases and salts. Acid – base properties of oxides, quantitative and qualitative analysis. Volumetric analysis, mole, molarity. Behaviour of electrolytes. Water, colligative properties. Oswald’s dilution law. Arrhenius, Bronsted – Lowry, Lewis concept and application. Buffers. Introduction to reaction rates. Equilibria and equilibrium constants. Common ion effects. Precipitation reactions. Nuclear binding energy, fission and fusion. Introduction of nuclear chemistry.
EPH012: HEAT, OPTICS, WAVES AND SOUND (3 CREDITS)
Temperature, heat work: heat capacities, second law, Carnot cycle, Thermal conductivity, Stefan’s law. Wave and light, mirrors, lenses, formation of images, thin lenses in contact. Types of waves. Reflection and refraction of waves, stationary waves, diffraction, fiber optics, dispersion, interference, coherence and polarization. Propagation of sound in solid, Liquids and gases. Poppler effect.
END012:ENGINEERING DRAWING II (2 CREDITS)
Dimensioning, sectional views, conventions, true lengths, technical sketching, civil, mechanical and electrical engineering drawing practice.
ELA012: WORKSHOP TECHNOLOGY AND PRACTICE II (2 CREDITS)
The Engineer in practice. Basic production Processes. Types of engineering workshops, including jobbing, batch and mass production. Engineering materials. Safety in engineering practice. Marking out and measurement in the workshop, machine shop technology and practice.
DMT012: COMPUTER SOFTWARE (2 CREDITS)
Definition: Operating systems, Application software, High level languages, Identify input and output units, Storage units and CPU (Central Processing Unit).
Different types of software: System software, Application software and Low and high-level languages. Their impact on the office environment.
DMT022: COMPUTER HARDWARE (3 CREDITS)
Identifying all different parts of the computer. Full description of all parts and their interaction within the system. Trouble shooting.
Main board types and identifications. Functions & components. System casing. Installing and Upgrading. Testing. Electronics basics. Static electricity. Power supply functions/connectors. Form factors. PC Ratings. Soft switches. G/Power signals. G/Power supply testing and trouble shooting. Blackouts. Power surges. Line noise. Spikes. System Bus types/ features. Questions and answers
Year Two
EMA 021: CALCULUS AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS (3 CREDITS)
Simple functions of a single real variable and their graphs, continuity, limit. Graphs of simple functions: polynomials, rational, trigonometric, etc. Rate of change, tangent and normal to a curve. Differentiation of functions. Rules of function differentiation. Stationary values of simple functions: integration by substitution and by parts – definite integrals, volume of revolution, and area of surface of revolution. Differential equations: formation of differential equation of first degree and first order of type: variables, separable, exact, homogenous and linear.
ECH 021: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (3 CREDITS)
Non-polar functional group chemistry: alkanes, alkynes; structure, physical properties, reactions and mechanisms, stereoisomerism. Benzene: structure and aromaticity. Introduction to electrophilic substitution reactions.
Polar functional group chemistry: hydroxyl group: alcohols and phenols; carbonyl group aldehydes and ketones; carbocyclic group – monocarboxylic acids derivatives, i.e. anhydrides. Acid halides, esters and amides; amino group – amines. Structures: physical properties, important methods of preparation and important methods of preparation and important reactions including mechanisms. Tests and importance. Fats and oils, amino acids, proteins, carbohydrates. Definitions, importance. Nomenclature and classifications, structure and reactions. Natural products, steroids, terpernoids alkaloids. Prostaglandis: definitions, importance and examples.
ELA021: WORKSHOP TECHNOLOGY AND PRACTICE (2 CREDITS)
Presentation of Experimental Data and Analysis. Technical Writing and Report presentation.
EPH021: ELECTROMAGNETISM AND MODERN PHYSICS (3 CREDITS)
Properties of ferrous metals and semi-conductors (silicon and Germanium). Quantum electrodynamics (Einstein’s theory and discovery). Electric field. Magnetic field. Young’s equations steady direct current, Kirchoff Laws. Capacitors, Alternating current and circuit. Electromagnetic induction, electricity and matter structure of atoms. Atomic theory, X-rays, Planck – Einstein quantum theory. Rutherford atom model, Bohr’s atom model. Hosenberg uncertainty principle, Isotopes, particle emission, gamma radiation, lasers, superconductivity.
DIPLOMA PROGRAMME IN MARINE DRILLING AND PRODUCTION TECHNOLOGY
Year One
DPT011: INTRODUCTION TO PETROLEUM ENGINEERING
The aim of the course is to provide students with a broad overview of introduction to petroleum engineering in order that advanced courses in subsequent years can be understood within a broader petroleum engineering context. This course covers introduction to petroleum drilling, completion and production, reservoir mechanics, fundamentals of rock and fluid properties, composition and PVT properties of petroleum fluids; basic physical and chemical properties of petroleum reservoir fluids related to reservoir processes and production. It also introduces decision-making and the petroleum business environment.
DPT013: INTRODUCTION TO PETROLEUM GEOLOGY
The Petroleum Geology section provides a detailed description of clastic and carbonate reservoir rocks, with the unifying theme being that reservoir location, shape and properties can be understood and predicted from knowledge of the environments in which the sediments forming the rocks were deposited, and the various processes which occur following deposition (diagenesis). The behaviour of fluids in reservoir rocks is covered next, with capillary pressure principles as a basic concept for understanding issues such as vertical and lateral distribution of fluids in a reservoir, seal capacity, and recovery efficiency. Volumetric reserve estimation is covered next, followed by discussions on enhanced oil recovery, unconventional reservoirs and the storage of carbon dioxide in reservoir rocks as a technique for greenhouse abatement.
DPT015: PRINCIPLES OF WELL CONSTRUCTION
Drilling team organization, Rig types, Rig systems, Petroleum geology, Completions, Casing and cementing, Directional drilling, Drilling fluids and solids control, Wellbore stability, Drill strings, BHAs and Drill bits.
DPT012: PETROLEUM ECONOMICS
Oil and gas business context, economic and business concepts, cash-flows and petroleum fiscal regimes, time-value of money, discounted cash flow, net present value and other economic metrics, case study and portfolio management. Economic Modeling, Decision Analysis, Exploration Analysis and Economics of Unconventional Resources.
DPT014: DRILLING AND WELL COMPLETION
Rotary Drilling Mechanics – the process, Water and Oil Base Mud, Routine Calculations, Drill String Design Basics, Rock Mechanics and Drill Bits, Hydraulics, Casing Design Basics (with supplemental material), Cement, Well Bore Architecture, Example Well, Pressure Control, Directional Drilling, Down Hole Motors.
DPT016: OFFSHORE /DEEPWATER DRILLING
introduction to Class, Deepwater Platform Floating Drilling Vessels Types of Motion Station Keeping Wellheads and BOP’s Drilling Risers, Motion Compensation Special Problems in Floating Drilling; Shallow Water Flows Dual Gradient Drilling Deepwater Drilling Fluids Drilling Hydraulics High Pressure Risers Pore Pressure and Fracture Pressure Prediction Deepwater Casing Design and Running Procedures Deepwater Cementing Deepwater Well Control.
DPT018: CASING DESIGN
Pipe Types, Loading Modes, Design Factors, Pipe Functions, Design Requirements, Pipe Mechanics, Pipe Designation – Size, Weight, Tolerances,Grade , Lengths Sour Service. Tension, Compression, Internal Yield Pressure, Collapse, Yield Strength and Threshold Stress, Service Life Design Load(s) Equations, Calculation Procedures, Summary of Equations: Burst, Collapse, Axial Load (Tension/Compression), Triaxial Equivalent Stress Intensity, Example String Designs and Production Casing.
Year Two
DPT021: WELL COMPLETIONS AND WORKOVERS
Completion design process; reservoir parameters and hydrostatics; well performance; service rig; wellbore and completion equipment; artificial lift equipment; completion and workover fluids; well testing; stimulation; primary and remedial cementing; sand scale and hydrates; wireline; and coiled tubing. Students to estimate production and completion data and develop a personal plan of action for completing and working over a well.
DPT023: REGULATORY ISSUES FOR THE OIL AND GAS INDUSTRY
Topics covered include fundamental law concepts; federal, state, and local rules and regulations regarding human, health, and environment related to the energy sector; air and water quality; solid and hazardous waste and materials; inactive and abandoned sites; underground storage tanks; environmental safety; roles of federal, state, and local regulatory agencies; regulatory compliance and enforcement related to the energy sector.
DPT025: PRODUCTION AND RECOVERY
Well production operations from exploration until the well is abandoned. Primary focus is on reservoirs, well completions, workovers, and stimulation, which are key and critical to producing operations.
DPT027: COMPUTER APPLICATIONS FOR THE OIL AND GAS INDUSTRY
Practice in the use of common computer applications, including Microsoft OS, Microsoft Office, and electronic media etiquette. Emphasis on the use of oil and gas industry specific applications. This course meets the division’s computer literacy requirements.
DPT022: PRODUCTION TECHNOLOGY
The term “production” here relates to the methods to extract fluid within the reservoir to the surface. Topics include: the major components of the production system options available to efficiently complete a well Use of Reservoir – Well – Facility flow modelling techniques available to enhance production from both reservoir and well design of appropriate procedures to ensure optimal initial production the process of delivering and treating reservoir and injection fluid at the surface
DPT024: INTRODUCTION TO RESERVOIR GEOPHYSICS
Petroleum Geophysics section presents an introduction to reflection seismology, the main geophysical method used in hydrocarbon exploration and development. After an outline of the various types of information that can be obtained using the method, the basic physics at its heart is described – the reflection of (sound) waves from interfaces within the earth, and the refraction and attenuation of these waves as they travel down and back up to the surface. The interpretation of the data to produce maps or models of the reflecting interfaces is covered, and the section concludes with a brief description of the data acquisition and processing required to produce the seismic images which the interpreter works with.
DPT026: ROCK GEOMECHANICS
The first part of the coursedeals with the fundamentals of rock mechanics. This includes theories of elasticity and failure mechanics, borehole stresses, and acoustic wave propagation. Fundamentals of the theory of poroelasticity will be explained. After that we will talk about methods for obtaining parameters that are relevant for rock mechanics field application, ranging from laboratory tests to borehole logs. In the last part of the course, we will discuss applications of rock mechanics in borehole stability, sand production, hydraulic fracturing and reservoir compaction/ reservoir subsidence.
DPT028: DRILLING FLUID/MUD ENGINEERING
Drillingfluid,functions,types,compositions,propertiesofmud,Fieldtest,Geology,Additives and contamination,Selectionof drillingfluidsandmud,Conditioningequipment,Mud calculations, Hydrostaticpressure,Volume,Weightrelated calculations during drilling.
DPT030: SURFACE PRODUCTION AND EQUIPMENT
Wellequipment,typicalwellheadassemblyand attachments,Casinghangers,Sealassembly,Typical Christmastreeassemblies,Componentsanddesignconsiderationsofwellheadequipmentandchoke, Introductionto subseaproductionsystem,Subseawellheadandcompletionaspects,SurfaceSafety Valve,chokesizing.
DPT034: LABORATORY PRACTICE
Drilling fluid geological and thixotropic properties, Drilling mud determination, salt content analysis, cementing operation, Sand content analysis, pH determination, ageing experiment, Processing of drilling additive s from local materials. Theinstructor’smanualshouldbepreparedseparatelyforindividualcomponentof this laboratorycourseandshouldbe namedas DrillingEngineering,ProductionEngineeringand ReservoirEngineering. TheInstructor’smanualshouldincludeAim,theory,procedure,figures,observations, calculations and results for every experiment.
DPT032: PETROLEUM GEOLOGY
Petroleum Prospecting, use of geological data reservoir rocks, reservoir fluids, traps, origin of Oil & Gas geology of the Niger Delta and Lake Chad Basin Geophysics.
DPT036: OFFSHORE DRILLING & PRODUCTION EQUIPMENT
Introduction, Outline of Rotary Drilling Method Offshore Drilling Structures: Technical Features of offshore Drilling, Mobile Bottom-supported Riggs, track up Drilling Rigs (Jack-up Rigs, self-elevating Drilling Rigs), Submersible Drilling Rigs (submersible Rigs, Swamp Barges), Tender-Assisted platforms & Tenders, Floating Offshore Drilling Rigs (floaters): Technologies required by floaters, Drills, Location surveys for offshore Drilling. Offshore Oil & Gas production systems, submersible Drilling rig, various Types of offshore platforms; Bottom-Supported platforms, Floating platform, Subsea production Systems, Subsea Christmas Trees, Subsea manifolds, Subsea Boosting and Processing, Subsea Control system, prospect of offshore production systems, Biographical sketches
DPT300: PROJECT
DIPLOMA IN INDUSTRIAL WELDING AND FABRICATION TECHNOLOGY
Year One
DWF011: INTRODUCTION TO DESIGN
History of design, the design process, Social/Environmental consideration, Design forFabrication, Careers in Design
DWF013 : FABRICATION TECHNIQUES
Shop safety, metrology, Machine Operation, Environmental Protection, Shop Related Careers
DWF012: INTRODUCTION TO SHOP PRACTICE
Material typesand properties, the Production Environment, Processing ofMaterials Careers in Production
DWF014: GRAPHICAL COMMUNICATION
Lettering and sketching, 2. Orthographic Views, 3D Pictorial Drawing, Working Drawings, Drafting, Related Careers.
Year Two
DWF041: INTRODUCTION TO CAD/CAM
Creating Entities, Display Manipulation, Modifying Entities, Dimensioning, Plotting, Computer Aided Manufacture (CAM)
DWF051 : THE DESIGN PROJECT
The Dosing Portfolio, Defining the Problem Generating Options, Selecting the BestOption Developing the solution, prototyping and testing, Evaluation and Redesign.
DWF071 : SAFETY IN WELDING ENGINEERING
Recognize health hazards relating to welding (fumes, Toxic gases, noise, radiation), recognize safetyhazards (electric shock, compressed gases, firs, welding in a confined space, welding on containers and piping, moving equipment) Recognize precaution to avoid injury, possess a working knowledge of safety and fire codes.
DWF052: BRAZING AND SOLDERING
Characteristic of Brazing and soldering, fluxes and substrates, capillary action, Wetting and Spreading, contact Angle, join clearance, viscosity, Liquids and Solidus Flow of Molten, Filler in Horizontal and vertical Join (Maximum penetration and rate), filler metal systems (sn-pb solders, ni and cu based alloys, ag-cu based brazed alloys) intermetallic compound formation.
DWF062: WELDING AND JOINING METALLURGY (3 CREDITS)
Crystal structure of Metals (FCC,, BCC, HCP, Unicells, Lattice, Parameter, c/a Ratio, atom, positions, Interstitial positions), Melting and Solidification, Phase Transformation and Phase, Diagrams (Eutectic, eutectoid, peritectic and monotectic, lever, rule calculation) Metallurgy and Welderbility of Typical Engineering Materials (Low carbon structural steel, cast iron, cast iron, stainless steels, nickel alloys, aluminum alloys, titanium alloys etc) Microstructure (eg. ferrous alloys – grain boundary ferrite, acicular ferrite, bainite, Martensite, austenite, delta ferrite, etc), and mechanical properties, Carbon Equivalent (CEIIW, PCM, Expressions, Alloying content and carbon content Effect) Hydrogen Assisted cracking (Heat-affected zone cracking, cold cracking) Based metal matching (eg. Electrodes with high strength steels) Solidification cracking(Segregation of Impurity atoms, shrinkage for consumables (Categories, all position, rutile, basic), Fluxmetal reactions (Oxygen and sulphur control in weld pool), Typical Temperature range of a heat source, Temperature Distribution in a weldment, HAZ Fromation, Multiple thermal experience, reheated weld metal properties, weld macro and Micro-graph interpretation, solidification Profile and preferred grain Orientation (epitaxial growth) Origin of weld Ripples, Special Attributes of Base Metal (as cast structure, deformation texture, oxide on flamecut surfaces), Thermal treatments (preheat, postheat, inter pass influence on weld cooling rate and residual stress distribution)Solid state transformation in welds (different forms of Ferrite bainite, and martensite, Sigma in stainless steel, guinier-preston type precipitate zones and again in aluminum alloys) Corrosion (Sensitization in stainless steel welds, stress corrosion cracking in welds)
DWF072 : WELDING PROCESSES AND CONTROL (3 CREDITS)
Are weldingprocesses (SMAW, GMAW, FCAW, GTAW, SAW, RAW), resistance welding processes (RW, high frequency RW), high energy density welding processes (LBS,EBW), cutting processes (OFC,CA, and PAC), Surfacing processing (SW,THSP). Solid state welding process (FRW, FW)
DWF082: STRESS CORROSION CRACKING OF MATERIALS (3 CREDITS)
Fundamentals of stress corrosion cracking (SCC), of Materials, PrimarilyMetals as one of the most dangerous type resulting in a material failure. Factors contributing to SCC from environmental, Metallurgical and mechanical aspects. Various testing techniques to conditions.Pipelines SCCunder near-neutral PHconditions as well as the mitigations and preventive measures.
DWF092 : WELDING DESIGN AND EQUIPMENT (3 CREDITS)
Structural fabrication Requirements, Sectional Properties, stressGradient, stress Triaxiality. Weld symbols, Hardness and Micro hardness (e.g. Across a weld cross-sectionTensile properties, Ductility, Toughness, Fillet Break Test (influence of secondphase andporosity) Duties fracture, Brittle Fracture, Fatigue (Influence of second phase high circle, and low circle), Temperature and strain Rate Effect.
DWF094: FUNDAMENTALS OF PIPELINE DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION(3 CREDITS)
The intent of this course is to provide the student with a comprehensive overview of the many and varied activities that are involved in developing and maintaining a pipelineinfrastructure to transport hydrocarbons in a cost-effective manner. The lecture material is presented in a logical sequence of a eight (8) blocks covering elementsof design/route selection, hydraulics, mechanical and geotechnical design, materials selection, construction and operation and maintenance.
DIPLOMA IN PROJECT MANAGEMENT TECHNOLOGY
Year One
PMT011: INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING MATERIALS
Atomic structure, molecular structure, classification of engineering materials — metals, ceramics, polymers, etc.
Metals: Extraction of metals, iron and steel making aluminum smelting and extraction and non-ferrous metals, e.g. tin.
Application and limitations of pure metals.
Crystal structures: Lattice unit, bravais lattice, symmetry, lattice planes and directions, miller indices, interplaner spacing, packing of spheres, simple cubic, body-centred cubic, face—centred cubic and hexagonal packing. Interstitial Sites: Sizes and distribution. Imperfections in crystal, surface and boundary defects, vacancies and interstitial. Dislocation twinning. Phase diagrams and alloy theory, heat treatment of carbon steels, Precipitation hardening. Non-ferrous engineering alloys, processing methods.
Mechanical Properties of materials: plastic deformation of a single crystal, stain hardening, stress-strain curves. Creep, toughness and resilience hardness. Principles of mechanical testing, impact, tensile, hardness, fatigue, creep and non-destructive tests, mechanism of fracture ductile. brittle transition, fatigue, electrical, optical and magnetic; properties of metal. Conduction and carriers, conductivity in metals, semi-conductors and insulators hall effect, magnetic circuit and magnetic properties. Emission, absorption, reflection, transmission and refraction.
Non-metallic materials: ceramics — structure, properties, processing and applications. Plastics related products, dispersion strengthened composite, fibre-reinforced V composites. Wood — softwood, hardwood, structures. Nigerian timbers – strength, properties and tests Environmental stability of material: corrosion — types of corrosion and corrosion control. Thermal degradation of polymers, dissolution and swilling, radiation damage.
Laboratory
Loading modes in tension compression, torsion and bending. Hardness measurement, stress-strain curves. Ductile and brittle behavior. Communication, sizing and compaction of properties
PMT013: PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT
Evolution management thought and practice, different schools of management thought, Management function and processes, Organizational management, classical and Neo-classical theories, Contemporary Organization Theories, management by objective.
PMT015: INTRODUCTION TO PROJECT MANAGEMENT
The nature of project Management: Choice of product Services; Market Research; Production Planning and Development; Choice of Technology; Technical Feasibility Assessment; Economic Analysis; Financial Feasibility Assessment; Evaluation of Infrastructural Facilities. Site selection: Social Cost/Benefit Analysis; Project Finance; Sources and Cost of Capital.
PMT017: BASIC ACCOUNTING
Book-keeping, preparations of ledger accounting, trial balance, profit and loss account, income and expenditure account and sheet, Analysis and interpretation of various financial and accounting statements, cost accounting, fixed and various costs, structural costs, Techniques for cost, estimation and control, Management accounting, Profitability planning and measurement.
PMT012: QUALITY MANAGEMENT & CONTROL
Concepts of quality control; Objectives of quality control; consequences of quality control; Costs associated with quality control; Manufacture quality; Inspection of purchased materials / Wild 377 and parts; the economics of quality control.
Acceptance sampling; the design of single acceptance, sampling plans; Double and multiple sampling.
Control charts: Types of control charts; the use of the “Average outing quality limit” (AOQL) of a single sampling table, the use of the ‘lot tolerance per cent defective’ (LTPD).
Computers in quality control dimension signals: The wait Accept or reject signals. People as inspectors; Item characteristic with a defined standard; Inspection of variables (i.e. measurement); inspection of attributes (i.e. assessment).
PMT018: INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRICAL TECHOLOGY
Basic electrical engineering: Basic Concepts: Conductors and insulators. Electrical Components, DC (Direct Current) Electrical Circuit; Ohms Law: Series Resistances. Resistances in Parallel Voltage Divider Circuits; current Divider circuits Inductance and Capacitance Circuits. Energy and Power in DC circuits.
Network Theorems: Kirchoffs Current Law; Kirchoffs Voltage Laws, Norton’s Theorem.
DC Transients: Linear Differential Equations; Charging a Capacitor, Current in R-L-C circuits. Alternation Current. Alternating current (AC); Sinusodal Alternating, Circuits — Current; Resistance / Inductance in AC-Circuit; Power circuits.
Electronics: Semiconductor Physics; The P-N junction, Rectifiers, Transistor Operation; Vacuum Tubes. Magnetic Fields and Circuits: Magnetic Fields; Induced voltage (Faraday’s Law), Energy stored in a magnetic Field. Measurements: Indicating Instruments; Ammeters, Voltmeters, Wheatstone bridge; AC bridge circuits. Transformers: Basic Parts; Transformer Operation; Transformer test. Voltage regulation, Auto-transformers.
DC Generators and Motors
Three-phase circuits — Three-phase voltages and currents star connection. Measurement of power in 3-phase circuit. alternators, AC Motors. The practice in Nigeria. Electrical installation: Generation and transmission of electricity; emergency power systems-megning types. uses. etc. Cables; wiring distributing and control equipment — transformers and converters. Electrical installation-design, planning and implementation; law/regulations and institutions. Installations-mains-power, lighting, electrical appliance, earthing/lightning protection, other installations-security, sound. etc. for different types of constructions/facilities e.g. for residential, industrial and other buildings/civil works.
PMT021: MATERIALS MANAGEMENT
Materials Purchase Management; Organization of materials purchasing department; purchase procedures and records; purchase price.
Material Control; ABC Analysis; determination of stock levels re-order quantity.
Stores organization; types of organization. centralized stores impress stores and decentralized stores; stores location and layout; classification and coding of materials.
Stores routine records; materials requisition control; receipts and issue of materials; stores material control records.
Perpetual inventory control system; Methods of valuing materials issue; materials ledger; methods of pricing materials issue; treatment of loss of materials in stores.
PMT023: FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
Managing short-term finance: working capital management. receivable management, Inventory management. cash management, sources of short-term and intermediate financing. Raising long-term funds, capital structure, common stock, fixed Income Securities, Term Loans, Internal Financing. Financial institutions in Nigeria and international financing institutions.
PMT025: INDUSTRIAL LOCATIONS
The approach to industrial location: plant location in context of industrial location; location factors; spatial economic analysis; Approach to theory; Critique and reform. The variable cost model; demand and time dimensions; operational models; Elements of Empirical analysis; Selected case studies; the impact of industrial activity; The spatial strategy of industrial development; case studies in industrial development planning.
PMT027: CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS
i) Fundamentals of construction materials science. Classification and Requirement for materials and products. Properties of materials and products. Evaluation of quality.
ii) Construction Materials and Products. Wood-General characteristics, Types of wood materials and product, Conversion, Defects and preservation seasoning, treatment.
iii) Stone — Rocks and minerals; inner structure and properties. Quarrying, milling and surface finishing types and properties of natural stone materials; maintenance/ preservative treatments of stone.
iv) Structural Clay products – classification, Raw materials and manufacturing processes. Main structural clay products and their properties, Metals — structure and properties. Ferrous and non-ferrous metals – basic manufacturing processes, protection against corrosion and fire.
v) Material and products based on mineral binders; Mineral binders-types, properties and application; Mortars and concretes. reinforce and concrete products. Asbestos-cement and other man-made materials and products.
vi) Synthetic polymers. Synthetic resins and Resin- based materials. Polymeric building materials and products — basic types and properties polymeric-based composites.
vii) Glass, Plastics and Rubbers— Manufacture. types and properties. Uses.
viii) Adhesives and types — natural; synthetic. thermosetting, rubber-based properties, manufacture and uses. Joining materials mortars, mastics and gaskets.
ix) Materials for External Works: landscaping grassing; erosion. Control/reclamation; roads and pavements; drainage.
PMT029: PRINCIPLES OF ENGINEERING SURVEY
Introduction to branches of surveying. principles of Survey practice, survey methods, Uses of basic surveying instruments e.g. Theodolite and levels. Lens. Measurement of distances, Angles. Compass and plane table. Bearings, theodolite traversing and computation. Adjustment of traverse leveling with Dumpy. Tilting and Automatic levels. Traverse computation, Area computation. Subsistence bar, Tachometric survey. Topographic surveying. Introduction to National grids.
Laboratory
Adjustment of theodolite and levels. Traversing, leveling, computation and plotting. Service load conditions; Shear strength, Including Cracking and Shear reinforcement; Bonding. Stress and development of Reinforcement; Design of one-way slabs; T-Sections in Bending; Continuous Slab-beam-Girder and Concrete joist floor system; Monolithic Bean-to-column joints; Retaining walls; members in compression and Bending.
PMT022: TAXATION
The fiscal systems; tax principles and concepts; tax incidence; income taxation; taxable income, tax relief, tax loopholes, personal income taxation. partnership. corporate taxation capital gains tax, the petroleum profits tax; capital transfer tax; excise tax.
PMT024: MARKETING MANAGEMENT
The role or marketing in today’s organization
Tasks and philosophies of Marketing Management
The marketing system; Applications to Nigeria
The distribution structure: Physical distribution Promotional strategy: Decisions; Brand strategy decisions Pricing decisions and policies.
PMT026: OPERATIONS RESEARCH I
History of operation research (O.R). Phases of an O.R. project O.R. and its systems orientation. Linear programming model (Graphical only). Sensitivity analysis. Applications. Some variations of linear programming — The transportation model and the Assignment model. F|ow-graph theory in general. Decision theory. Inventory control (Deterministic Case Only.)
PMT028: PROJECT PLANNING & CONTROL
The project concept and project idea formulation; Scope of project evaluation; Project location and Exhaustive cost analysis; Break-down of project cost and investment expenditures. Types of benefits and benefit analysis; Profitability analysis; Simple rate of return method, pay- back period method; net present value method and internal rate of return; Financial analysis; Social consideration and assessment of success factors; Disaggregated planning; Project in the context of Development Planning; Cost benefit analysis of projects; Programming Project execution; applications of Critical path method (CPM) and Projects; Project control.
PMT032: STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT
Overview of strategic management, evolution concepts and processes. Purposes of strategic management and its relationship with business planning. Methods of future planning including the role of information technology;
SWOT (Strength, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats) analysis and evaluation. Competitive advantages — its meaning in different markets and industries of nations and the implication for organization success; approaches of competitive advantage used by organizations and management of other countries and lessons for Nigeria. Strategies formulation, implementation and evaluation. The future for nations, organizations and workforce (including management). Forecasting trends and developments using qualitative and quantitative methods.
PMT034: PROJECT DESIGN & E. l. A.
Scientific Design Methodology: An appreciation of the process of engineering design, and of systematic procedures and tools usable in the design process, with reference to mechanical systems and devices. Topics include systematic problem definition, search for possible solutions, statistical analysis of stress/strength interference. Experiment planning techniques, optimum design for minimum weight and cost, management of the design process.
Design Project: Students will be required to conduct a design project under supervision using the techniques presented above and taken at least to a workable layout drawing of the device. The design should involve simple mechanical systems (e.g. testing and assembling devices, heat drives, etc.) for a specified duty, analyze its operating conditions and after considering the design criteria, choose between potential solutions. Reports submitted by students should contain all calculations, a comparison of potential solutions, justification for the design finally chosen and instruction on detail design, manufacture, testing and use.
PMT036: MAINTENANCE MANAGEMENT
Concepts and importance of maintenance: Definitions, Causes of defects/failures/malfunctions in the built environment and machines, maintenance needs, resources for maintenance, maintenance manuals/equipment, etc. Types/Nature of Maintenance: Maintenance systems — planned, unplanned, ad-hoc, etc.
Alterations and improvements
Maintenance Economics: Specifications, measurements, measurement and pricing of maintenance work, cost-in- use, life-cycle cost.
Planning and financing of Maintenance Work: Maintenance management —contract and direct labour, organization, maintenance contracts and agreements, quantitative technique in maintenance management, repairs: Repairs. Replacement policies
PMT038: MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMS
Introduction to information system in business. Fundamentals of information system, solving business problem with information system. Overview of computer hardware, software, telecommunication and database management system analysis and design.
MIS Application in business and management – information system for business operation. management decision making and support and strategic advantage. Managing information technology enterprise.
DIPLOMA IN COMPUTING AND COMPUTER TECHNOLOGY
Year One
DCT011: COMPUTER FUNDAMENTALS
Introduction (Basic Introduction of Computers, History of Computers and its Generation, Importance of Computers in 21st Century), Hardware, (Introduction of Basic Hardware Components, Power, Supply, casing, motherboard, CPU, chipset, real time clock, BIOS Memories, Storage Devices, Magnetic (Hard “Disk, floppy disk) optical (CDs and DVDs, Pen drive), (RAM, ROM, EPROM, VRAM, Parallel, Ports, serial ports, interfacing (IDE, SATA, DATA, ATAPC), Programs: Operating System and its importance (DOS, Windows, UNEX, LINUX, Introduction Only), Application Programs and its importance (Office, Package, Photo Editing Package) Device Inverse Concepts, Concept of Internet: Browser Programme, (Internet explorer, Moxilla etc.) Concept of WHP, WWW. FTP, Email concepts, connect to internet from home using modern, very basic concept of small office, college networking).
DCT013: COMPUTER PROGRAMMING IN C++
Computer Evolution (History and Generations): Computer Hardware (Block diagram of digital computer), Computer Software and its types. Programming languages, Problem Solving Method: Problem analogies, Algorithm Development and Flowcharting, Programming. Compilation and Execution, Debugging and Testing, Program Documentation, Introduction to C: Features of C, Data types in C, Operators and Expression, Basic Elements in C, Basic Input and Output: Character Input/Output. Formatted Input/Output. Programs, using Input/output Statements. StructuralProgramming Fundamentals Sequential Structure, Repetitive Structure, Selective Structure, Programs using Decision making and Looping. Functions: Function Component (function prototypes, call and Definition), Return Statement Passing by Value and Passing by Reference, Storage Classes, local, Global and Static Storage Class) Recursion, Arrays, Pointers and Strings, Structure, Files and Files Handling in ‘C’
CCT015: ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
Electromagnetism and Electromagnetic Induction: Definition of magnetic field, magnetic flux, flux density, field intensity and permeability of magnetic materials, magnetic field due to current carrying conductors, force on a current carrying conductors, Faraday’s Law of Electromagneticinduction, induced EMF, Lenz’s Law, magnetic circuit concept analogy to electric circuit, hysteresis loop for magnetic, materials hard and soft mantic material, Electric Circuit Fundamentals: Electric current and voltage, circuit elements (Resistor, inductor, Capacitor), Voltage and current sources, independent and dependent sources, series and parallel circuit, Electric Power and Energy, DC Circuit analogies: Ohm’s law. Kirchoff’s current and voltage Laws’ Theveniin’s theorem, Norton’s theorem, supposition theorem, maximum power transfer theorem loop and model equations for electric networks, Single Phase AC Circuit Analysis: Generation of Sinusoidal EMF: Instantaneous, peak average and RMS values, Application of Coupler number; phasor representation of AC quantifiers, AC excitation for RL. RC and RLC Circuits and Resonance in RLC series Circuit power in AC circuit, active power, reactive power, apparent power, power trainable and power factor, 3-phase AC Circuit Generation of 3-phase sinusoidal voltages Advantages of 3-phase system, line and phase quantities (Current voltage star and delta connection of 3-phase source and load; power in 3-phase circuit, Electric Machines: Transformers, Construction and working principle of single phase transformers, DC motor and Generator (Construction, generation of voltage and torque production) single phase AC motor 3 – phase induction motor construction and working principle) 3-phase synchronous generator (construction and work principles), cells and batteries. Types, series and parallel connection of cells.
CCT012: LOGIC CIRCUITS
Introduction: Analog Signal and Digital Signal Advantages of Digital over Analog Signals representation of Digital Signal, Application of Digital Signal, Number Systems and Codes: Two State of Devices, Decimal System, Binary Number system. Octal Number Systems, Hexadecimal Number System, Conversion among different number systems. Systems: Hexadecimal Number System, Conversion among different number systems, Fractions, Conversion, BCD Code, Gay Code, Alphanumeric Code, Arithmetic Logic Operations: Binary Arithmetic 9’ and 10’ complement method. 1’s complement method. Logic Gates: Basic Gates (AND, OR, NOT), Universal Gates (NAND, NOR) Exclusive Gates (SOR, SNOR), Logic Equations, Truth Tables Combination of Logic Gates, Building Logic Circuit from Logic Equations, Forming Logic Equations from Logic Circuits, Boolean Functions and Logic Simplification: Boolean Algebra and its propensities/law, Boolean Expression in Logic Gates, Simplification of Boolean Expressions DeMorgan’s Theorems, Sum of Production (SOP), Combinational Logic Circuits (Adders, Subractors, Encoders, Decoders, Multiplexers, Demultiplexers, Sequential Logic Circuits.
CCT014: OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING
Introduction to Object oriented programming, introduction to C++Language Basics Character set, tokens(Keyboards, Identifiers, operators) connection, variable declaration, data type, input/output basic, processor directives, central structures, array, pointer, string, dynamic memory allocation, functions, construct, structure and union, Object and class, Overloading operators, Inheritances, virtual functions, input/output streams and files, Templates.
CCT016: WEB TECHNOLOGY AND PROGRAMMING
Introduction internet and Web: History and growth of internet and Web, Introduction to WWW.Web browsers and search engines, internet protocols and Applications, Overview of various internet and web technologies, HTML/DHTML: introduction, Objectives, Structures of HTML/DHTML, Document, switching between opened windows and Browser (container tag, Empty tag, Attribute), Basic Toys of HTML, HTML, HEAD, TITLE, BODY (Surfing the fore colour and Background colour, Background image, Background sound) Heading Tag (H1 to H6) and attributes (ALIGN); FONT tag and Attributes (size 1 to 7 levels, BASEFONT, small, big, colour) Paragraph formatting (p) Break line BR; comment HTML (); formatting Text; Ordered List UL; Address Tag, Web page Authoring Using HT All Tables (Creating Tables, Border, TH, TR, TD, CELLSPACING, CELLPADDING WIDTH, COLSPAN, CAPTION, ALIGN, CENTRE); FRAMES (PERCENTAGE dimensions, relative dimension, framer – Src, Frameborder, height and Width, creating two or more rows from es creating two or more columns from , NO FRAMES>;, Forms: Definition: Use written to a file, submitted to a database such as MSA-Access or MySqI; E-nailed to someone in particular, forms involved two-way communication, form Tags FORM,
SELECT NAME, SIZE, MULTIPLE/SINGLE>, TEXTAREA NAME ROWS COLS>, AREA>, METHOD, CHECKBOX, HIDDEN, IMAGE, RADIO, RESET, SUBMIT, INPUT HTMLEditors and Tools: Dream weavers, Microsoft front page etc. Abode Photoshop and Flash etc., Adding sounds and Animation to the Page (Using embed tag), Document Object Models: Concept and Importance of Documents Object Model, Dynamic HTML Documents and Document object Model, Cascading Style Sheets. CCT018: DATA MINING AND DATA WAREHOUSE An Overview of Database Systems (Review of tradition processing and its limitation) Evolution of Databases Systems (Database application and users, Main characteristics of the Database), Database Languages (Structured Query Language (SQL), Functional Dependencies, Data Manipulation Language), DataWarehousing (data warehousing Design (definition, star schemes, fact tables, dimensions dimension hierarchies Data Mart), OLAP and Data Mining (Definition) Data Warehouse Physical Design (Partitioning, Parallelism Compression, Indexes) Data Warehouse Construction (Introduction, Data extraction (Data Transformation, Loading and Refreshing), OLAP Architecture (SQL, Extraction for OLAP), Data Mining Model (Statistical, statistical Method (Probability, Averaging, Means Square Deviation ) Maximum Likely Hood Methods, Bayesian Decision Tree (Information Gain, Decision Tree Learning, Classification), Neural network (Supervised nueral networks, perception, Back) Cluster Analysis (Means, Hierarchical clustering) Data Mining Application (Techniques for mining large databases (Text mining web mining. Visual data mining)Data mining support in SOL Server, Oracle, Data Mining Standards, Privacy and Security Issues. Year Two CCT021: WEB TECHNOLOGY AND PROGRAMMING II Introduction (Server side and Clint Side Scripting, Advantages and Disadvantages), Internet introduction Client Side Scripting using Java Script (Introduction of internet technology, Adding Java script to HTML page, Java script fundamental, Java Script Data types, Variables and operators, Functions and control structure, Object based programming with Java Script and Event handling, Image, event and form objects, Form validation, JQuery), VISUAL BASIC .NET and Server Side Scripting using ASP. NET (Introduction to DOT NET Technology, Object oriented programming with server side scripting, Intro to object oriented programming in visual basis .net, Procedures, Advanced data types, Control Structures, Exception handling, Inheritance, Interfaces and collection, Introducing ASP.NET, Web site adding and configuring server controls, Exploring specialized server controls, Create custom web controls, Input validation and site management, Programming the web application, Customizing and personalizing a web application, Globalization and accessibility, Using ASP.NET, AJAX control toolkit), Database (Introduction to SQL, Database design, Queries and Data Manipulation, Grouping and aggregating data, Views, Transactions, Stored procedures and triggers, Privileges and security), Database Connectivity (Connecting server side script to database, Making SQL queries, Fetching data sets getting data about data, Multiple connections, Building in error checking, Creating SQL database with server side scripting, Displaying queries in tables, Building forms from queries), XML (Introduction, XML syntax rules, XML Validator, XML Browsers, XML XSL, Introduction to XSLT, XSLT template, value of, for each, sort, if , choose, Introduction to Document Type Definition, XML schema, Ado.NET and XML with ASP.N), Database (Basic Concept of AJAX, SOAP and other web services) CCT023: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Basic computer architecture (Introduction (History of computer architecture, Overview of computer organization, Memory Hierarchy and cache, External Memory, Organization of hard disk), Instruction codes (Stored program organization-Indirect address, Computer Registers, Common bus system, Computer instruction, Instruction set), Timing and Control-Instruction Cycle (Fetch and decode, Limiting errors), Type of Instruction (Register reference Instruction, Memory reference instruction, Input and output interrupt)), Micro programmed control (Basic Computer Design of Accumulator (Control of AC register, Adder and logic circuit, ALU organization), Control Memory-Address Sequencing (Conditional Branching, Mapping of Instruction-Subroutines), Micro program (Symbolic Micro program, Binary Micro program), Design of control unit (Basic requirement of control unit, Structure of control unit, Hard wired control unit, Micro program sequencer)), Central processing Unit (General Register Organization (Control word. Stack organization. Instruction, Formats-Addressing Modes), Data transfer and Manipulation (Data Transfer Instructions, Data Manipulation Instructions, Arithmetic Instructions, Logical and Bit Manipulation Instructions, Shift Instructions), Program control (Status bit conditions, Conditional Branch Instructions, Subroutine Call and Return, Program Interrupt, Types of Interrupts), Reduced Instruction set Computer (RISC) ( CISC Characteristics, RISC Characteristics, Overlapped Register, Windows-Berkeley RISC), Computer arithmetic and memory organization (Addition and Subtraction (Hardware Implementation, Hardware Algorithm, Addition and Subtraction with Signed-2’s Complement), Data Multiplication Algorithms (Booth Multiplication Algorithm, Array Multiplier), Division Algorithms (Divide overflow, Hardware Algorithm, Floating Point Arithmetic Operations, Basic considerations-Register Configuration), Memory concept (Main Memory, Auxiliary Memory, Associative Memory) Memory Hardware Organization (Match Logic, Read operation and Write operation, Cache memory, Associative Mapping, Direct Mapping, Set-Associative Mapping, Writing into Cache-Cache Initialization, Virtual Memory-Address space and Memory space), Address mapping Using Pages (Associative Memory page table, Page Replacement-Memory Management Hardware, Segmented-Page Mapping)), Pipeline, vector processing and multiprocessors (Parallel Processing (Pipelining-Arithmetic, Pipeline-Instruction), Pipeline Examples (Four Segment Instruction Pipeline, Data Dependency, Handling of Branch Instructions, etc.), Vector Processing (Vector operations, Matrix Multiplication, Memory Interleaving, Super computers. array processors, Attached Array Processor-SIMD Array processor)). CCT025: COMPUTER REPAIRS AND MAINTENANCE I Introduction to Computer (Definition of Computer, Introduction to Data, Introduction to Program, Introduction to information, Hardware and Software. Classification of Computer (Analog, Digital, Hybrid Computer, Super, Mainframe, Micro-computer, General and Special Purpose Computer), Role of Computer (Education, Health, Industries, Transportation, Research, Business) Computer History and Generation, System Case (Style and size, Form Factors, Switches, LEDs, Drive bay, Power Supply (Ratings, Working Principle, Block Diagram, SMPS Concept), Mother Board and System Devices (Form factor, Parts, Chipset and controller, Buses, BIOS), Unit 8. Input Devices: (1) (Keyboard,Mouse,Light pen,and other devices), Processor (Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), Control Unit, Register, Machine Cycle (Instruction cycle and Execution cycle), Buses (Data bus, Address Bus, Control Bus) CCT027: MICROPROCESSORS Introduction to Microprocessor (History of computer development, Analog and digital computer, Microprocessor, microcomputer, microcontroller, Stored program concept and von-Neumann’s architecture, General architecture of a microcomputer system showing control buses, History of x86 microprocessors, Block diagram of a typical microprocessor and microcontroller, Programming languages, Instruction set of microprocessors, Introduction to Simple as Possible (SAP1,SAP2,SAP3) computers), Microprocessor architecture and the instruction set (Internal architecture of 8085 microprocessor, Instruction and data formats, Instruction classifications, Addressing modes in 8085, 8085 Instruction set), Assembly language programming for 8085 (Introduction to assembly language and assemblers, Simple assembly language programs, Programs using loops, counters, delays, Table processing, Subroutine and stack, Code conversion ASCII/BCD/Binary), Interfacing I/O and memory devices (4.1. 8085 machine cycles and bus timing (Fetch and execute cycles, Memory read/write machine cycle,I/O read/write machine cycle), Address Decoding (Unique and non-unique address decoding, Address decoding for I/O and memory devices), Interfacing I/O devices (Interfacing Input Devices, Interfacing Output Devices, Address decoding using block decoders, Interfacing Memory-mapped I/O), Memory Interfacing (Memory structure and its requirement, RAM and ROM chips, Address decoding using NAND and block decoders), Direct memory access, 8085 Interrupt processing (Programmed I/O, Interrupt Driven I/O, The 8085 Interrupt, 8085 Vectored Interrupts, Restart and software instructions), Introduction to general purpose programmable peripheral devices (8255 Programmable Peripheral Interface, 8254(8253) Programmable Interval Timer, 8259 Programmable Interrupt Controller, 8251 USART). CCT029: ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS Basic Passive Devices: R, C and L (Construction, types, color coding and characteristics), Introduction to electron vacuum tube (Diode, Triode and Pentode), Semiconductor Devices (Energy levels, valence and conduction bands, conduction of electrons andholes in solids, Intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductor devices (Si), impurities, doping, majority and minor charge carries in P – type and N – type materials. Definition ischaracteristic, Diffusion and drift currents – definition and characteristics, PN Junction and depletion layer and potential barrier – definition andcharacteristics, Forward and reverse biasing of PN junction diode – IV characteristics, principles of operation, and effects of temperature and junction capacitance, Forward and reverse breakdown of PN junction diode – Zener and avalanche effects – Principles of operation and IV characteristics, Electrical analysis of PN junction diode with IV characteristics and mathematical expressions with equivalent model circuit diagrams, Power Supplies (Basic rectifying circuits – Types, working principles, characteristics and applications, Analysis of simple DC voltage power supplies – Principles, characteristics and ripple (voltages) factors, Simple voltage regulation using Zener diodes – Principles, circuits, characteristics and application, Pripolar Junction Transistors (NPN and PNP) – Types, construction, workingprinciple as an amplifier and characteristics (Classification of amplifiers: CB, CE and CC amplifier circuits – Working principles, basic circuits to investigate input and output IV characteristics and their results, Other characteristics of BJT – Saturation and cutoff modes: Definition, circuits, principles and characteristics, Types of amplifier circuits: Class A, class B and class C – Definition, characteristics and applications, Specifications and data book) Field Effect Transistor (JFET and MOSFETS) – Types, construction, working principles as an amplifier and characteristics (Basic circuits for investigating input and output IV characteristics – Working principles, characteristics and applications, Saturation, cut off breakdown and ohmic regions of operation – Investigationof IV characteristics curves, Specifications and data book), Special Semiconductor Devices – Working principles, functional circuits, characteristics and applications ( UJT, PUT, SCR, Diar and Triac, Photo voltaic effects and solar cells, Photodiode, phototransistor, LED, LDR, optocouplers and isolators, Tunnel diode, schottyky diode, GaAs Transistors, MESFET, Charge coupled devices, Hall effects, solid state relay ad thermister. CCT030: COMPUTER REPAIRS AND MAINTENANCE II Storage Devices (Primary Storage Devices (RAM (Types, Speed, Access and Time, Size, Error Detection andCorrection, Logical Memory Layout)), ROM (PROM, EPROM, EEPROM), Cache Memory, Flash Memory), Secondary Storage Devices (Hard disk (Brief History, Construction and Operation, Speed, Disk Geometry, Track, Cylinder and sectors, Capacity, Partitioning and Formatting, Interface IDE/ATA/SATA/SCSI), Compact Disk (CD/DVD, Color book Specification, Performance and Reliability, CD/R-W principle, interface), Video Display (Video modes, resolution, color, size), Monitors (CRT (Simple working Principle), LCD), Printers (Impact, non-impact, Static or Laser, Non-static or inkjet and bubble jet), UPS (Introduction to UPS), Unit 15. System Care (Preventive Maintenance: General system care factors, Cooling and Ventilation, Power protection, Data loss and virus protection), Data problem detection (Virus detection and protection, Background of viruses, Virus scanning and antivirus software), Backup and Disaster Recovery (Risk of data, Backup methods devices and media, Backup scheduling, Recovery of data) CCT032: COMPUTER NETWORKS Introduction to computer network (Introduction, definition, features, issues, Applications of computer networks), Network architecture (Network topologies, Network types: LAN, MAN, WAN, Layered network architecture, protocols, interfaces, services, OSI Reference model, TCP/IP Reference model, Standardization organizations), Network hardware and software (Network workstation and server: hardware and software requirements, Client server and peer-to-peer model, Network devices: Repeater, Hub, NIC, Bridge, Switch, Router, Gateway), Physical layer (Digital signals, line coding formats, Transmission impairment: attenuation, distortion, noise, interference, Channel bandwidth and throughput; propagation time, transmission time, Transmission media (Guided: coaxial, twisted-pair, fiber-optic Unguided: radio, microwaves, infrared)), Data link layer (Introduction to data link layer and its issues, Flow control at data link layer, Error control issues at data link layer, Data link layer protocols: HDLC, PPP), LAN architecture/standards (Introduction to LAN standards and architecture, Media access control, MAC address, CSMA/CD, Token ring, Token bus and IEEE 802.3, 802.4, 802.5, Introduction to wireless LAN, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Wi-Max), Network Layer (Internetworking, Switching: Circuit switching and packet switching, Addressing issues at network layer, IP address; Different classes; Private and Public address, Subnet mask and Subnetting; Classless addressing; Network address translation (NAT), Routing and its necessity; static and dynamic routing; interior and exterior routing, Introduction to dynamic routing protocols: RIP. IGRP, OSPF, Network layer protocols: ARP, RARP, IP, ICMP, Introduction to IPv6 and its necessity), Transport layer (Transport layer issues: Congestion control, Flow control and Quality of service, Transport layer addressing, sockets, Segmentation and reassembly, Connection oriented and connectionless service Transport layer protocols: TCP, and UDP, Application Layer (Application layer and its function, Electronic mail: SMTP; File transfer: FTP; Dynamic host configuration protocol (DHCP), DNS, HTTP, and WWW; Network security (Cryptography, Digital signature, Firewalls, Virtual private network) CCT034: DATA STRUCTURE AND ALGORITHM Introduction (Abstract Data Type (Definition, Methods of Specifying ADT, ADT data structure) Array implementation of Data Structure), Stack and Queue (Stack as an ADT and OperationContinuous implementation of Stack with varying and fixed TOS),Application of Stack (Converting Infix to Post fix expression, Evaluating Post Fix expression), Queue as an ADT and Operation (Definition, Algorithm of Enqueue and dequeue, Linear Queue, Circular Queue, Priority Queue, Applications of Queue)), Link list as an ADT (Definition, Structure of link list, Advantage and disadvantages of link list, Operations in Singly Linked list (Insertion at the beginning and end, after the node, before the node, Deletion at the beginning and end, after the node, before the node), Doubly linked list (Definition,Structure of doubly liked list, Insertion at the beginning and end, after the node, before the node, Deletion at the beginning and end, after the node, before the node, Advantages and disadvantages)), Recursion (Definition, Properties of recursion, TOH and its solution, Solution of Fibonacci sequence and factorial), Trees (Tree concepts, Binary tree, Application of binary tree, Node representation, Operation in Binary Tree Insertion, Deletion), Algorithm of tree search, Tree traversals (Pre order, In order, Post order), Height, level and depth of tree and its importance, AVL balance tree (Definition, Detection of unbalance, Single and double rotation in balancing), B-tree (Definition, Structure of B tree, Applications), Sorting (Definition, Types of sortingInternal and external), Algorithm of exchange sort, Algorithm of bubble sort, Algorithm of queue sort, Algorithm of insertion sort, Algorithm of selection, Search (Sequential search, Binary search, Tree search, Definition, Components of searching, Hashing (Definition,Hash function and hash table, Collision resolution algorithm, Open Addressing, Linear and quadratic probing, Chaining)), Graph (Definition, Components of Graph, Vertices and edges, Directed and Undirected, Connected and Unconnected, Path and Cycle, Adjacency sets and tables, Array based, Linked based and mixed implementation, Graph traversal and spanning forests (Forest and tree, Tree edges, Forward edges, Cross edges, Back edges, Algorithm of graph traversal, Depth First traversal, Breadth First traversal)). CCT036: DATA BASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM Introduction (Understand and apply the terminologies: data, information, flat-file, database,database systems, database management system, data warehouse, datamining; Early data processing; DBMS: evolution, characteristics of databaseapproach, ANSI/SPARC database architecture, advantages anddisadvantages; Data independence; data abstraction; Centralized andDistributed database, Database administrator, Data dictionary), Data models (Definition, Type of data models: record based, object based and physical; Hierarchical, Networks, Relational, Object oriented and ER models; Logical design of database: ER Diagram and Schema Diagram. Entities and entitiessets, attributes and its types, Relationship and mappings), Relation Database (Relational Database: Structure and its importance; The Relational algebra: fundamental operations- selection, projection, cartesian product, set difference, union, intersection, join, division and rename. Relation Calculus: tuple and domain calculus; Schemas, instances and views), Relational Languages (Structure Query Language: component and types; Data Definition Language: data types, size and constraints; Data Manipulation Language: operators,functions, clauses, subqueries, QBE and GQBE), Relational Database Design (Introduction, constraints and its types; Functional dependency: multivalued and join dependencies, Normalization: Normal Forms – 1NF, 2NF, 3NF andBCNF; Trigger), Security (Needs of security, Security and integrity violations, Access control, Authorization, Security and Views, Encryption and decryption), Query Processing (Introduction to query processing, Query interpretation, Equivalence of expressions, Query Optimization, Join strategies, Query decomposition), Filing and File Structure (Needs of filing; Overview of storage devices: cache, main memory; flash memory, magnetic disk and buffer management; Organization of records: Fixed length and variable length, blocks; File organizations: The sequential and the indexed sequential file organizations; Hash and Heap piling), Crash Recovery (Introduction to crash recovery and its importance, Failure classification, Backup-recovery, Log-based recovery, Shadow paging), Concurrency Control (Transaction and Transaction processing, Transaction model, Scheduling and serializability, Locking and Lock based protocols, Time-stamping-based Protocols CCT038: COMPUTER GRAPHICS Introduction (Introduction and history of computer graphics, Applications of computer graphics, Application in the CAD and CAM), Two-dimensional Graphics (Line drawing methods – DDA and Bresenham algorithms, Circle and ellipse drawing algorithms, Review of matrix operations – addition and multiplication, Two-dimensional transformations – translation, rotation, scaling and reflection), Three-dimensional Graphics (Projection of 3D objects onto 2D display devices, Parallel and perspective projection, D transformations – translation, rotation, scaling, refection, Methods of 3D object representation – polygon tables and polygon surfaces, Introduction to hidden lien and surface detection techniques, Introduction to lighting models, Introduction to shading models – constant shading, Gouraud shading and Phong shading), Graphics Hardware (Input hardware – mouse, keyboard, light pen, touch screen, tablets, scanner, Output hardware – monitors, plotters, printers, Raster and vector display technology- principles and characteristics, Raster display – cathode ray tube and color production techniques, Principle and operation of LCD monitor, Fundamentals of Animation Techniques (Animation sequences, Key-frame and parameterized systems, Morphing and simulating acceleration), Graphical User Interface Design (Need and application of GUI, Windows, icons, menu and other graphical interface items, Principles of interactive user dialogs – managing skill levels, consistency, loading, off memory, error handling, continuous feedback, default values, use of, metaphors, color blindness), Web Graphics Design (Introduction to graphics file formats, Principles of web graphics design – browser safe colors, size, resolution, background, anti-aliasing, Introduction to Graphics Design Packages (Need of machine independent graphic packages, Type and purposes of graphics packages, Desirable features of a graphics design package, Examples of graphics packages and libraries) CCT040: ARTIFICIAL INTELLINGENCE Goals in problem-solving (Goal schemas, use in planning, Concept of non-linear planning, Means–end analysis, Production rules systems, forward and backward chaining, Mycin-style probabilities and its application), Intelligence (Introduction of intelligence, Modeling, humans vs. engineering performance, representing intelligence using and acquiring knowledge), Knowledge Representation (Logic, Semantic networks, Predicate calculus, Frames), Inference and Reasoning (Inference, theorems, Deduction and truth, maintenance, Heuristic search, Statespace representations, game playing. Reasoning about uncertainty Probability, Bayesian networks, Case-based Reasoning), Machine Learning (Concepts of learning (based on Winston), Learning by analogy, Inductive bias, learning, Neural networks, Genetic algorithms, Explanation based learning, Boltzmann Machines), Application of artificial intelligence (Neural networks: Network Structure, Adaline, Madaline, Perceptron, Multilayer Perceptron, Radial Basis Function, Hopfield network, Kohonen Network, Elastic net model, back-propagation), Expert Systems (Architecture of an expert systems, Knowledge acquisition, induction, Knowledge representation, Declarative knowledge, Procedural knowledge, Knowledge elicitation techniques, Intelligent editing programs, Development of expert systems), Natural language Processing (Levels of analysis: Phonetic, syntactic, semantic, pragmatic, Machine Vision: Bottom-up approach, edge extraction, line detection, line labeling, shape recognition, image interpretation, need for top down, hypothesis-driven approaches. CCT042: E – COMMERCE Introduction (History of e-Commerce, how e-commerce works, e-Business, Categories of e- Commerce Applications, global trading environment & adoption of ecommerce, Differentiate between traditional and e-Commerce, advantages and disadvantages of e-Commerce), Business Models of e-Commerce (Major challenges of B2B e-Commerce, Business to Business (B2B), development of B2B e-Commerce, types of B2B market, the e Hub concept, difference between B2C and B2B e-Commerce, C2C or P2P, C2B, B2G, e- Procurement), B2B e-Commerce and EDI (Electronic Data Interchange(EDI), components of EDI, protocol, EDI standards, Data standards used in EDI, Electronic funds transfer, e-Marketing, ad network, XML and its applications), Mobile Commerce (Application of M-commerce, advantage of m-commerce, wireless application protocol, WAP Browser, Mobile Commerce architecture),(Technology for Online business (IT Infrastructure, Internet, Intranet, Extranet, VPN, Firewall, Cryptography, Digital signature, Digital certificate, Hypertext, Hypermedia, HTTP), Electronic payment system (EPS) (Online banking, types of EPS, security requirement of EPS, Secure socket layer (SSL), secure electronic transaction (SET), payment gateway, online payment processing, and payment processing Network), Security Issues in e-Commerce (e-Commerce Security Issues, Risks Involved in e-Commerce, protecting e- Commerce System, e-Commerce Security tools, biometric, Client server Network security, data and message security), Legal and Ethical Issues (Issues related to e-Commerce, Legal issues, ethical issues, taxation), Cyber law (Aims of cyber law, salient provisions of cyber law, Contracting and contract enforcement), Introduction to Entrepreneurship (Entrepreneurship development, Entrepreneur Vs. Entrepreneurship, Entrepreneur Vs. Manager, attributes and characteristics of a successful Entrepreneur, Entrepreneurial Culture.351

Recent Comments